As a professional...
Tin can manufacturers share the whole process of tin can manufacturing
1. The tin box originated in Bohemia (in today's Czech Republic and Slovakia). In 1810, the world's first tin can was invented by the British. In 1847, the United States invented a can-making machine to replace manual can-making. In the 1990s, tin cans gradually entered people's lives when the technology of can making was improved and the speed of can making was accelerated. The development of global tinplate has roughly gone through the following stages:
Before 1914, during the development period of hot-rolled single-sheet hot-tinned sheets, the production of tin-plated sheets took the lead in Britain.
From 1918 to 1940, tinplate was produced in coil form. The United States dominates the production of tinplate.
From 1939 to 1960, the electroplating process was developed, and tin plating production began to develop in developing countries.
Since 1960, Japan has become the second largest tinplate producer after the United States, and many countries in the third world have built many electroplating units.
In 2015, the annual consumption of tinned iron in China was about 4 million tons.

2. The characteristics of tinned iron
The opacity of tin-plated iron, and the tin on the iron will interact with the oxygen remaining in the iron box during filling, which reduces the possibility of oxidation for the package contents and is essential for its preservation; plating The metal ductility of tin iron makes it possible to achieve high-precision and high-speed production of more complex can types. The good rigidity enables the tin cans produced to withstand collisions, vibrations and stacking, which is convenient for transportation and storage; it is easy to recycle and recycle. The environmental protection of tin-plated iron is also better than that of plastic and paper packaging. The above characteristics have made tin-plated iron packaging boxes chosen by many companies as their product packaging materials. The most important thing is that its metallic texture will reflect the preciousness that plastic packaging and paper packaging do not possess.
Tin-plated iron not only has excellent performance as a packaging material, but also tin-plated iron can be made into different shapes, making tin can packaging containers more varied and promoting the growth of product sales. It can be said that tin-plated tin can packaging is a creative labor product that combines artistic and technical features.
3. Tinned iron is an environmentally friendly packaging material
Existing containers include tin cans, aluminum cans, paper and plastic containers. These containers have different recycling characteristics, but tin cans are better than other packaging materials in the recycling process.
1) Making tin cans with low pollution
Tin-plated iron, the main raw material in tin cans, is actually environmentally sound and can be decomposed naturally. When tin cans exist in the natural environment, they can be naturally oxidized to return to the original iron oxide state and return to nature. Therefore, the stacking of waste tin cans can be decomposed by time and will not remain and cause environmental pollution. At the same time, there is no need to cut down trees to make tin cans, which will not damage the ecological balance.
2) Tin cans are recyclable
Tin cans themselves have a feature that other packaging materials don’t have—the ability to be adsorbed by magnets. In this way, a magnetic separator can be used to separate tin cans from waste by magnetic force. This feature can be used to easily achieve recycling. The effect of 90% tin cans in garbage. The invention of the environmental protection cover not only makes the use of tin cans safer and more hygienic, but also effectively reduces the amount of garbage, which has direct and obvious benefits for recycling operations.
3) The process of making tin cans saves resources
In terms of removing other pollution residues on tin cans, shredder equipment has been developed, which can effectively remove more than 98% of the pollutants and provide good-quality scrap iron. In addition, the United States also pointed out that the existence of aluminum easy-opening lids is beneficial to scrap iron remanufacturing, because it can reduce the amount of hot metal used in steelmaking and reduce the overall cost of steel manufacturing. In addition, in terms of energy saving, the report pointed out that compared with iron ore production, the use of tin-plated iron scraps to produce steel can save about 230m3 of natural gas per ton of scrap iron scraps. Therefore, the recycling process of iron cans can reduce the impact on the world. The impact of sexual environment and energy is in line with future product trends.
4. Thickness of materials commonly used for tin can packaging
The thickness of commonly used tin-plated iron is basically divided into 0.19mm, 0.21mm, 0.23mm, 0.25mm and 0.28mm.
5. Common materials for tin cans
Common materials include smooth iron, frosted iron and high-gloss iron.
6. Introduction to the conventional hardness and application of tinned iron
, The Rockwell hardness value of tinned iron (HR-30T) is between 46 and 52T, suitable for processing deep drawing cans or nozzles.
, The Rockwell hardness value of tinned iron (HR-30T) is between 50 and 56T. It is suitable for making medium-level deep drawing cans, and is generally used for tin cans with certain requirements for deep drawing.
, The Rockwell hardness value of tinned iron (HR-30T) is between T2 and T3. It is more commonly used in the field of miscellaneous cans, and is used as can lid, can body or bottom.
, The Rockwell hardness of tinned iron (HR-30T) is between 54 and 60T. It is generally used for empty can bodies, can lids or crown caps.
, The Rockwell hardness of tinned iron (HR-30T) is between 58 and 64, which is suitable for making can bodies or bottle caps with high hardness requirements.
, The Rockwell hardness of tinned iron (HR-30T) is between 62 and 68, which is suitable for making large cans or can lids, as well as beer and carbonated beverage lids with large internal pressure.
, The Rockwell hardness of tinned iron (HR-30T) is between 70 and 76, suitable for making independent lids for beer and carbonated beverages.
, The Rockwell hardness of tinned iron (HR-30T) is between 73 and 79, which is suitable for making large can bodies or can lids.
, Rockwell hardness of tinned iron (HR-30T) is between 74 and 80, suitable for making beer and carbonated drinks
7. Introduction to the amount of tinned iron plating
The amount of tin plated on the surface of tinned iron is expressed by the weight of tin plated per unit area, in g/m2. The amount of tin plating is one of the indicators that determine the corrosion resistance of tin cans. According to the different requirements of the cans, tin-plated iron with different tinning amount can be used. The higher the amount of tin plating, the thicker the thickness of the tin plating layer, indicating the better the gloss of the tinplate. At the same time, tinplate with a thicker tinned layer is more prone to scratches during can making and has a higher loss rate.
8. Introduction of tin can production process
1.) List of traditional tin can processes
Compared with welded cans such as milk powder cans and beverage cans, miscellaneous cans have unique shapes, variable sizes, and a small number of orders in a single batch. Therefore, most miscellaneous cans projects are mainly manufactured by manual lines, that is, produced by employees operating punching machines. The following is the traditional can making process:
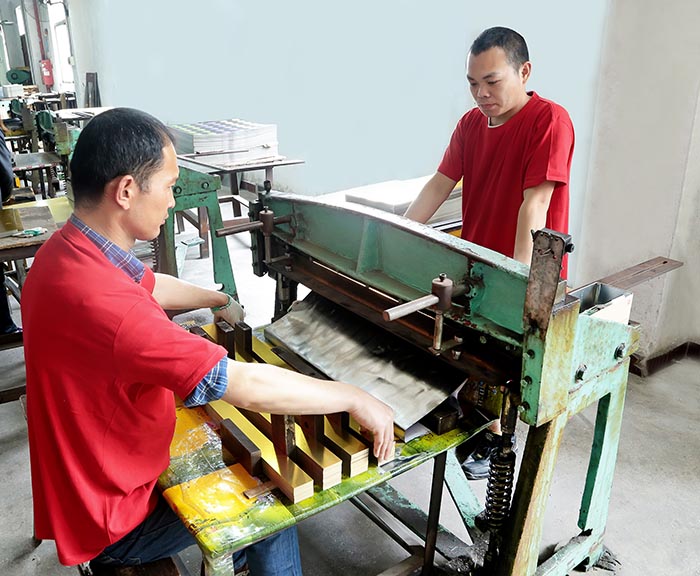
2) Introduction to cutting iron
As shown in the figure below, it is necessary to cut the tinplate tape into a sheet of iron that is convenient for printing. Usually, the size of the cut iron sheet should be less than or equal to 1060*960mm, which is the maximum size that the iron printing machine can accept.

3) Introduction to Printing Iron
Now most tin cans are printed with exquisite patterns, making tin cans not only play a role in food preservation, but also a decorative appearance. The tin-plated iron printing process is completed on the iron printing production line. The iron printing production line is generally composed of a feeding device, an offset printing unit, a coating unit, a drying room, and a film collecting device.
Tin-plated iron printing is transferred to the surface of the iron sheet through the principle of water and ink balance under the action of the appropriate printing pressure by the cylinder.
According to the design effect of the printing pattern, there will be two pretreatment methods before tinplate printing: one is over-white and the other is printing white ink. Too white can be tinned, that is, a layer of printing iron paint called white can be applied to tin plated iron. In white ink printing, white ink is printed on local areas of the tin-plated iron through the PS plate (according to the design document, white ink is printed where the pattern is required for color printing).
White is the base color of all pictures, with high brightness. After adding other high-energy hues, the brightness of each hue can be increased to form a color gradation. However, the two different pretreatments of over-white dicing and printing white ink will bring different printing effects:
, Over-white coloring: the color of the printed pattern is more saturated and brighter; the coating thickness of the white coloring is 3~4 times thicker than that of the white ink, and it has good whiteness and fullness than the white ink, and it is flat and smooth, and has enough luster degree.
, Printing white ink: Partially has iron penetration effect (you can see the lines of tin-plated iron where white ink is not printed); In order to make white ink adhere to tin-plated iron well, tin-plated iron must be printed before white ink Apply a layer of transparent primer.
Therefore, in the full-page printing, that is, the entire tinplate is printed, the pretreatment method of white can be selected. If you want to reflect the texture of iron, choose the pretreatment method of printing white ink.
Whether it is white-coated or white ink, the pre-processed iron sheet must be dried in an oven before it can be printed in the next stage.
According to the design documents, make a printed negative (usually four negatives of red, yellow, blue, and black, and sometimes a white negative), and then expose the negative on the PS plate (aluminum lithographic printing plate coated with photosensitive resin layer) , PS version is divided into positive PS version and negative PS version.
, Positive PS plate production steps: photodegradable diazonium compound is used as the photosensitive material, and the positive negative film is used as the original plate for printing. When the blank part is exposed to ultraviolet rays during printing, the sensitizer will be decomposed and will be diluted by alkali
The solution is wiped off. Because the image on the positive picture blocks light, the sensitizer will not decompose, and the sensitizer left on the PS plate has good lipophilicity, which becomes the basis of the graphic part of the printing plate.
, Negative PS plate production steps: photopolymerizable diazonium compound as the photosensitive material, and print the plate with a negative negative film. The sensitizer in the graphic part of the printing plate is cross-linked into a network structure and becomes hard under the irradiation of ultraviolet rays.
It becomes the basis of lipophilic image meaning.
The main difference between the positive PS plate and the negative PS plate is the photosensitive effect. Others are similar, and the positive PS plate is generally used.
After the PS plate is made, it is installed on the printing plate roller, and the printing pattern on the PS plate is transferred to the tin-plated iron under the action of a suitable printing pressure with the blanket cylinder and the impression cylinder.
The two-color machine can print 2 colors at a time, and each printing must be baked at a high temperature to make the ink solvent volatilize and the film is cured.
After the tin-plated iron is printed, a layer of surface protection oil is needed to increase the scratch resistance of the printed iron (tin-plated iron after printing), and at the same time increase a certain degree of hardness, so that the printed surface coating has a certain flexibility and Corrosion resistance. Different surface protection oils will give the iron box a different look and feel. The following are commonly used protective oils:
Varnish: Good color retention performance, can improve the vividness of printed colors and make the tin box higher gloss, in line with the traditional aesthetic habits of consumers.
Dumb oil: make the surface of the printed iron matte, have a paper texture, and have an elegant decorative effect.
Over-light stamping matte: You can also apply a layer of varnish on the stamping iron, partially stamping matte oil, the difference in gloss and touch, and highlight the key information through contrast.
Explosive oil: the surface of the printed iron has irregular explosive lines, which are crystal-like transparent scales. The reflection of light makes the exquisite printed patterns rich in three-dimensionality, a feeling of rustling, and sometimes a color-changing effect, which is very ornamental Sex.
Pearlescent oil: Let the surface of the iron box have a layer of luster like small water droplets, set off the brilliance and brightness of the printed graphics.
Orange peel oil: It will give the printed iron a corresponding touch, a bit like the lines on the surface of orange peel.
Rubber oil: With this oil, it feels soft to the touch, and there is no iron feeling at all.
The following are the renderings of various oils:

For tin cans of general shape, considering both quality and cost, it is most appropriate to use two-color printing (two-color printing has higher printing efficiency than monochrome printing, and printing quality is better than four-color printing). The best two-color machine currently used is Japan's FUJI printed wire. F 453 is the latest model of FUJI printed wire.
3) Cutting material
Because it is manual can making, it is necessary to cut the printed iron of 1060X960mm (the size of the printing press cylinder) according to the layout size, so that the staff can punch the can. This process is completed by the staff operating the shearing machine.

4) Stamping
Tinned iron has good ductility and can be stamped into cans of various shapes. A tin can is usually composed of a lid and a can body. Let's take a look at the common structure and technology of the can lid and the can body.
The following are several common lids: (independent lid, hinged lid, ordinary lid with inner and outer rolls)

Independent lid Hinged lid Outer roll lid
The following are several common can bodies: (buckle bottom, gong bottom, stretch bottom)

Buckle bottom gong bottom stretch bottom
Buckle bottom: If you don't want a protruding side at the bottom of the tank, choose a buckle bottom.
The bottom of the gong: If you want better sealing and there are protruding lines around the can, please choose the bottom of the gong.
Stretch bottom: two-piece metal box with small size, most of which use stretch bottom; common stationery boxes generally also have stretch bottom structure.
Except that tin cans with simple structure and large production volume are produced by automatic lines, other tin cans with more complex structure and small production volume are manually stamped.
A tin can, no matter how big or small, is made by multiple stamping processes, at least eight or nine processes are required, and as many as twenty or thirty processes. The number of procedures has nothing to do with the size of the tin can, mainly depends on the structure and complexity of the tin can. The can-making is: According to the structure of the tin can, the mold master makes the corresponding mold, and the worker presses the printed iron through the mold. Some tin cans seem to be similar, but due to the difference in individual structures, the order of the stamping process and the number of processes in the production process are different. But the basic process of iron box stamping is: can lid (tank bottom): cutting-flashing-coiling; can body: cutting corners-bending-punching bone-connecting bone-buckle bottom (gong bottom)-curling. Below we introduce the production process of tobacco tin cans, so that everyone can roughly understand the stamping process of can making, and it is better to go to the can production workshop to understand it on the spot.
Tobacco tin can production process:
The cigarette box is composed of two parts, a lid and a body, and the two parts are connected by twisting, and the rotation function is realized. The manufacturing process of the can lid and the can body are basically the same, and the bottom is buckled. The following mainly introduces the production process of the can body

Cut angle:
The printing iron is cut and cut into iron sheets of the same size as the printed document. Before making cans, cut off the square and beveled iron materials at the four corners of the iron sheet (if not cut, there will be three layers of iron at the joint, which is not conducive to curling. Cut into square and triangle respectively. It is to ensure that the joints remain smooth and free of gaps).

Because the inner curling line and the buckle (gong) bottom curling require different sizes, the shape and size of the corresponding cut corners will be different.
Sculpture:
Place the iron sheet on the engraving mold, and use the pressure of the punch to make the iron sheet partially protrude to form an engraving.
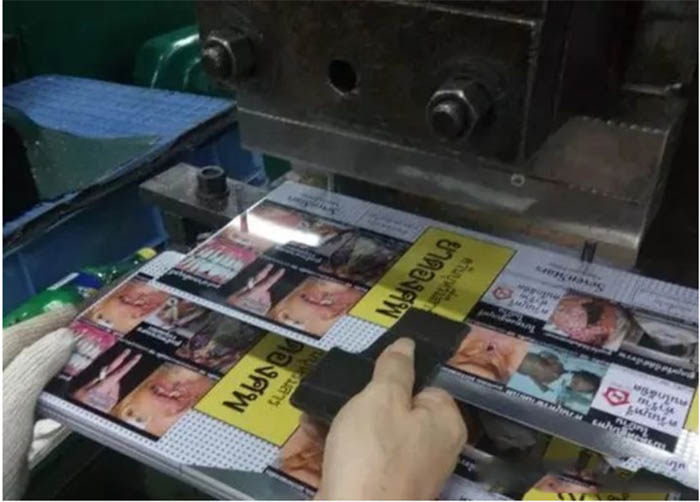

Secondary cutting:
The cigarette case is an oblique opening cigarette case, and the excess iron material needs to be punched and cut. Like ordinary round cans and square cans, there is no such process.
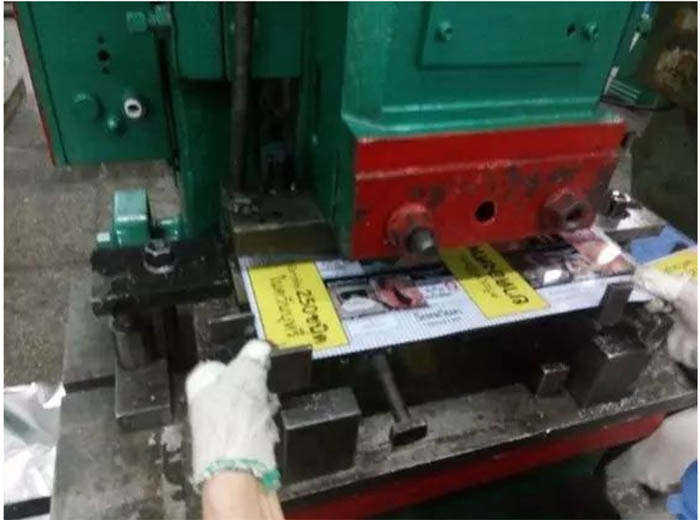

Pre-bending:
Put the section that needs to be buckled into the punching machine for punching, so that there is a slight bend on the side, in preparation for the buckle.
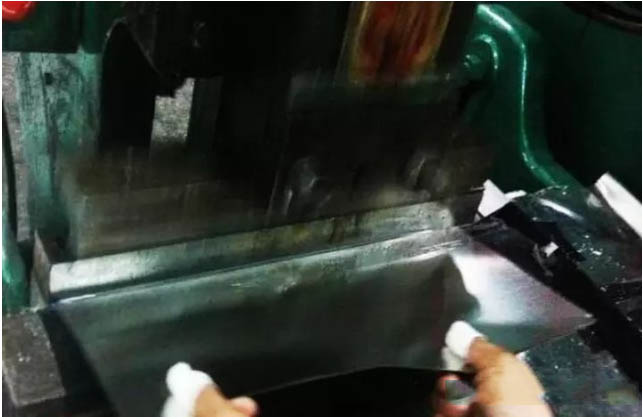

Bend:
According to the designed iron box size, after measuring the size, a workbench that can bend quickly and accurately is made.
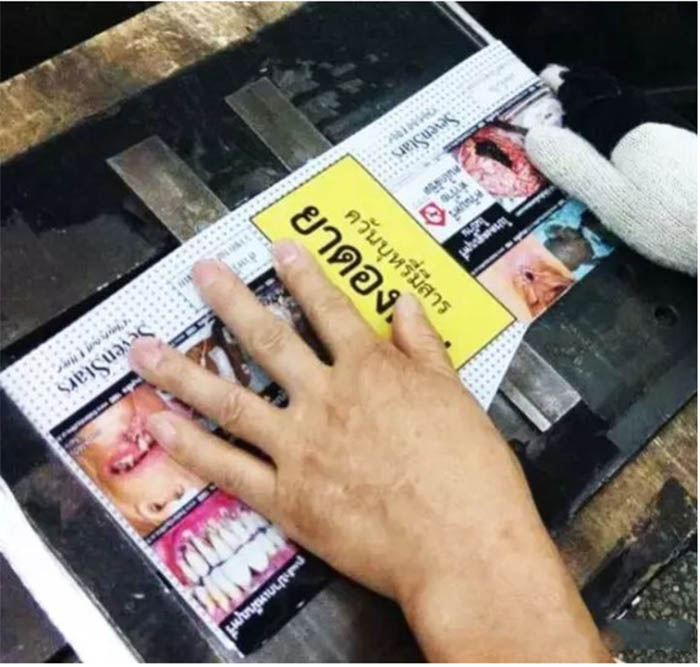
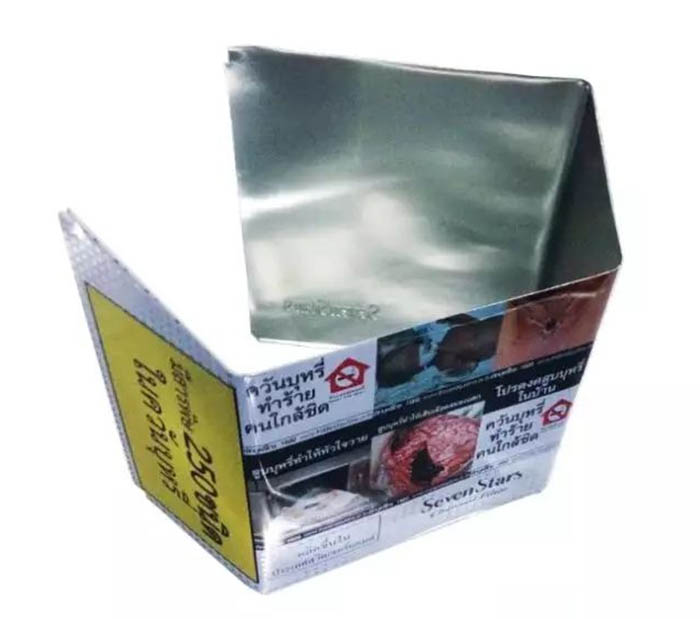


After bending over, the shape of the iron sheet
Bone:
Put the left and right ends of the iron sheet into the mold for punching, so that the side has a hook-shaped structure. Also known as "Bone Fighting". The hook structure at both ends is different, and the name is also different.
A hook-shaped structure with the sides of the square corners cut off is called "bone setting"
A hook-shaped structure with beveled edges, called "anti-bone"
Bones:
The two hook-shaped structures are "hooked" together and pressed tightly.

The tin cans are made by a set of molds. Generally, the tin cans Bone and bones are to be completed in two stations
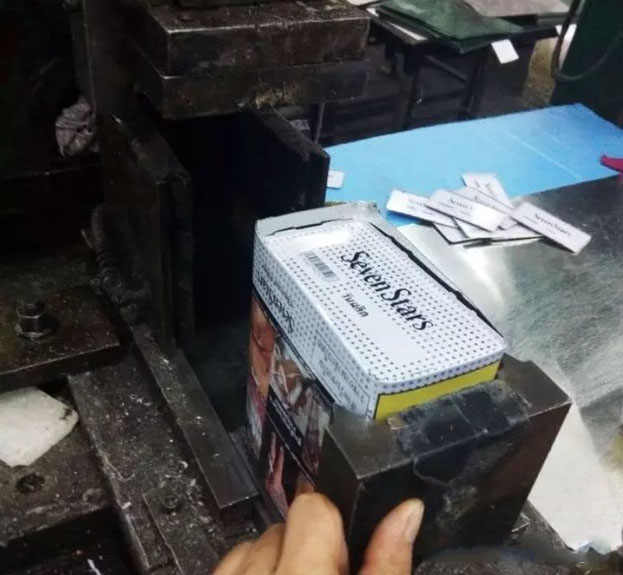
Buckle bottom:
Put the can body and the pre-stamped bottom into the mold together, and then punch. There is a groove in the mold, which will bend the iron sheet slightly by stamping, and do pre-bending treatment for the inner curling of the can body.

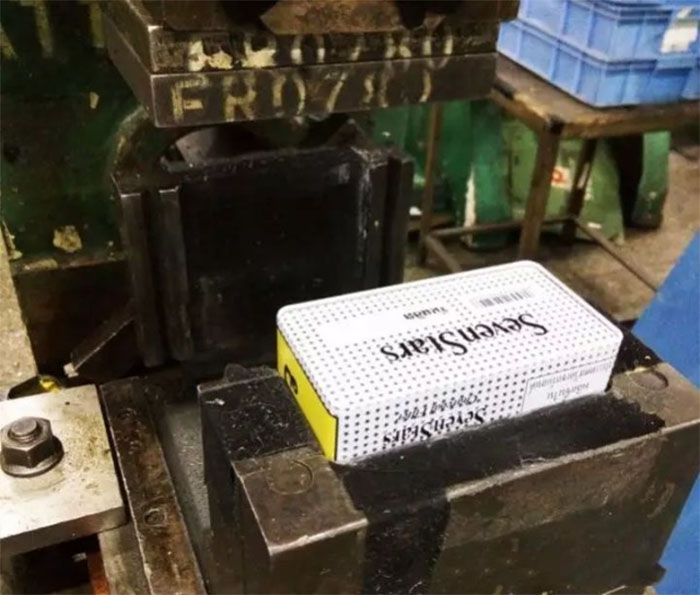
crimping:
Put the can body into the mold for punching.

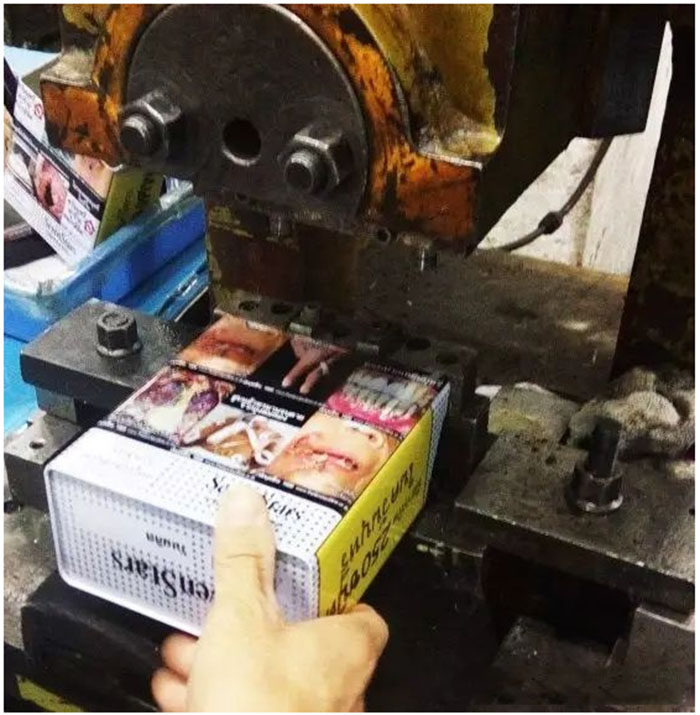
Strike position:
Use die stamping to make tin cans appear reaming holes.

The above is the production process of the can body. After the can body and the lid are sent to the packaging workshop for cleaning, the iron wire is used to connect the two. Finally, the cigarette case is put into the black plastic inner support, and it can be packed and sealed, waiting for shipment.
5) Cleaning and assembly
The tin cans stamped in the production workshop will be sent to the dust-free workshop for cleaning and assembly. Packers use medical alcohol to clean the tin cans.
There are many tin cans that need to be assembled after being stamped to be the finished product on the shelf. In addition to tin cans with hinged connections, there are also double wires for round cans, rhinestones inlaid on the surface of the tin boxes, ribbons tied or pasted on the tin cans, mirrors, handles and plastic toys are assembled on the tin cans Wait. It should be noted that the process of assembling belts and metal buckles to tin cans that require rivets to save labor costs are stamped by machines in the stamping workshop.
6) Packing and storage
The canning supplier will negotiate with the customer on the tin can packing form and carton type (single-pit carton, double-pit carton and three-pit carton). After confirming the type of carton and whether the tin can needs to be covered with a protective plastic bag before packing, customize the carton. Put the cleaned and assembled iron boxes into custom-made cartons and send them to the inventory warehouse for delivery to customers.

.png)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)












Latest comments